Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, increasing their risk of stroke. For those seeking an alternative to lifelong blood thinners, the WATCHMAN procedure offers a minimally invasive solution. This article will delve into the details of the WATCHMAN procedure, its benefits and potential risks, and help you understand if it may be the right treatment option for you or a loved one.
Key Takeaways
The WATCHMAN procedure is a minimally invasive solution for atrial fibrillation which seals the left atrial appendage to reduce stroke risk.
Candidates are patients with non-valvular AFib who desire an alternative to blood thinners
Benefits include minimized stroke risk & improved quality of life, potential risks should be discussed before making a decision, and choose provider w/ expertise in WATCHMAN procedures for optimal outcomes.
Understanding the WATCHMAN Procedure
The WATCHMAN left atrial appendage occlusion procedure is a minimally invasive solution for stroke risk reduction in atrial fibrillation. It uses a small, umbrella-shaped device to seal the left atrial appendage, thereby minimizing the risk of blood clots and stroke. Atrial fibrillation, a heart rhythm disorder, is more prevalent in individuals over the age of 65, and particularly those with:
hypertension
diabetes
sleep apnea
other cardiac conditions
When this condition remains untreated, it can result in harmful blood clots developing in the left atrial appendage. These clots may then travel to other parts of the body, potentially causing a stroke. Patients with atrial fibrillation are 5x more likely to have a stroke then patients without atrial fibrillation.
The Role of Left Atrial Appendage in Blood Clot Formation
The left atrial appendage (LAA) is a small sac-like extension of the left atrium where blood can accumulate and form clots in patients with atrial fibrillation. It has been observed that blood can coagulate in the left atrial appendage, resulting in the formation of thrombus, which can then increase the risk of stroke or peripheral embolism.
It has been estimated that over 95% of strokes due to atrial fibrillation are due to thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage. Left atrial appendage closure is a procedure that aims to reduce this risk by sealing off the LAA.
The link between the left atrial appendage and stroke risk highlights the necessity of managing blood clot formation in atrial fibrillation patients to prevent blood clots and reduce risk of stroke.
How the WATCHMAN Device Prevents Blood Clots
The WATCHMAN device is:
a small, parachute-shaped atrial appendage closure device approximately the size of a quarter
designed to prevent the formation of blood clots in the left atrial appendage (LAA)
implanted into the left atrial appendage, creating a seal that prevents the formation of blood clots that could travel through the blood vessel to the brain.
The WATCHMAN device seals the left atrial appendage, offering an effective method to lower stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation, reducing the need for strong blood thinning medications.
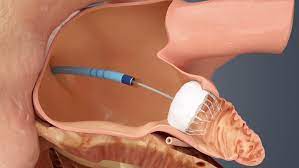
Candidates for the WATCHMAN Procedure
Patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation who require an alternative to blood thinners, to lower their risk of stroke, are eligible for the WATCHMAN procedure. This may include those with a history of serious bleeding while taking blood thinners, or patients with a lifestyle or occupation that could present challenges with taking blood thinners.
The WATCHMAN procedure is a dependable and effective method to decrease stroke likelihood, especially in individuals unsuited for long-term blood thinning medication. The WATCHMAN procedure has been FDA approved since 2015, and over 300,000 implants have been performed worldwide.
The WATCHMAN Procedure Step-by-Step
The WATCHMAN procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia, the WATCHMAN procedure involves:
Inserting a delivery catheter through a small incision in the leg, entering through the femoral vein
Guiding it into the heart using x-ray and ultrasound imaging
Inserting the device into the left atrial appendage using the delivery catheter
Once the WATCHMAN Device is in position in the LAA, its frame and mesh covering expand to accommodate the size of the left atrial appendage opening. Several steps are involved to determine if the expanded watchman device is satisfactorily placed in the LAA prior to release of the device from the catheter delivery system. Ultrasound devices or TEE are typically used during the procedure to ensure the device is well positioned in the LAA prior to device release from the catheter delivery system.
The procedure is minimally invasive and needs to be done only once. Many patients are able to go home the same day of the procedure. The WATCHMAN procedure, typically completed in about an hour, offers a quick and minimally invasive strategy for preventing strokes.
Recovery and Post-WATCHMAN Care
Following the WATCHMAN Device implantation, patient will usually need to lay in a recovery bed for 2-4 hours post procedure. For my patients, most patients are able to go home the same day of the procedure, although a small number of patients may spend the night in the hospital.
The recovery process includes period of limited physical activity.
I usually tell patients to take it easy for 3 days, meaning no prolonged standing or walking. After 3 days most normal activities are fine, although I council my patient to refrain from strenuous activities such as heavy lifting or exercise for 1 week. It’s essential for patients to attend follow-up appointments with their physician to ensure proper healing and monitor the device’s effectiveness in reducing stroke risk.
Activity Restrictions After WATCHMAN Procedure
It is advised that patients abstain from strenuous activity for a week post-WATCHMAN procedure to avoid complications and ensure proper healing.
Additionally, patients should arrange for a ride home from the hospital following the procedure, as they may still be experiencing the effects of general anesthesia.
Medication Management After WATCHMAN Procedure
Following the WATCHMAN procedure, the following medications are typically prescribed:
Some patients may still need to take stronger blood thinner (such as Eliquis or Xarelto) for a short period after the watchman procedure, usually around 45 days.
Alternatively, many patients can stop stronger blood thinning medications immediately post procedure and switch to dual anti-platelet therapy (recommendation usually involves taking a low dose aspirin and a second medication called clopidogrel) for approximately 6 months.
6 months after a WATCHMAN procedure, most patients require only a low dose daily aspirin.
The exact medication regimen should be determined based on the patient’s individual condition and risk factors, ensuring optimal stroke prevention and recovery.
Benefits and Risks of the WATCHMAN Procedure
The WATCHMAN procedure offers numerous advantages, including:
Minimized risk of stroke
Less invasive approach compared to open-heart surgery
Improved quality of life for patients with atrial fibrillation
Reduced reliance on blood thinners and associated risks
However, the WATCHMAN procedure is not without potential risks and complications. Some risks and complications from the WATCHMAN procedure can include:
The lining of the LAA is thin, so it is possible for the device to perforate the heart tissue, resulting in emergency heart surgery. This is an uncommon, but very severe complication of the procedure. In a previous study of over 38,000 patients, the risk of perforation requiring correction was 1.39%
Because this procedure is done under a general anesthetic, there are risks for reactions to the anesthetic medications.
There is a very small risk for infection at the site of the catheter insertion in the leg. Infections can delay healing time.
The device can dislodge from its intended position and embolize to other parts of the body. This risk is very low. Reports rates of embolization are far below 1%, usually around 0.3%
Your Complete Guide To AFib: The Essential Manual For Every Patient With Atrial Fibrillation
Expertise in WATCHMAN Procedures: Choosing the Right Provider
Choosing a provider with WATCHMAN procedure expertise, assures top-quality care and outcomes for patients opting for this treatment. It is advisable to evaluate factors such as the reputation of the medical center and the qualifications of the healthcare professionals involved in the procedure.
Researching medical centers in your area that offer the WATCHMAN Implant procedure and utilizing online resources can help you identify potential medical centers and make an informed decision about your care. Opting for a medical center with a wealth of experience and proficiency in the WATCHMAN procedure guarantees you receive the best care and optimal outcomes.
Learn more about WATCHMAN and find an implanting physician near you here
Summary
In conclusion, the WATCHMAN procedure is a minimally invasive treatment for atrial fibrillation that reduces stroke risk and provides an alternative to long-term blood thinner use. With proper preparation, expert care, and adherence to post-procedure instructions, patients can experience a quick recovery and improved quality of life. If you or a loved one is considering the WATCHMAN procedure, it is crucial to consult with an experienced healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcome and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the reason for the watchman procedure?
The WATCHMAN procedure is a minimally invasive, one-time implantation designed to close off the left atrial appendage (LAA) in order to reduce the risk of stroke caused by blood clots. The device is inserted into the heart through a delivery catheter placed through a vein in the leg. It is primarily used for patients who are at risk for stroke but also at high risk for bleeding events or complications due to chronic anticoagulation.
Is the watchman procedure a major surgery?
The watchman procedure is minimally invasive and is not considered a major surgery, as it involves inserting a device through a small incision in the upper leg.
Does watchman get rid of AFib?
Watchman is a permanent treatment option that can reduce stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. It permanently closes off the left atrial appendage, and typically takes one hour or less to implant, making it an effective AFib solution for stroke risk reduction.
However, it does not reduce or get rid of AFib. Atrial fibrillation treatment such as medications, procedures, or lifestyle modifications are still needed to improve symptoms of AFib.
What does the watchman do?
The WATCHMAN device prevents blood clots from forming in the left atrial appendage, helping to protect against strokes for patients with atrial fibrillation.
How long does the WATCHMAN procedure typically take to complete?
The WATCHMAN procedure typically takes around an hour to complete.
Who should not get a WATCHMAN procedure?
Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of the WATCHMAN Implant with their doctor before deciding if it is the right treatment for them.
The Best Atrial Fibrillation Book
Your Complete Guide To AFib: The Essential Manual For Every Patient With Atrial Fibrillation

Shop AFib Products on Amazon
KardiaMobile 6-Lead Personal EKG Monitor – Six Views of The Heart – Detects AFib and Irregular Arrhythmias – Instant Results in 30 Seconds – Works with Most Smartphones - FSA/HSA Eligible
13% Off
KardiaMobile 1-Lead Personal EKG Monitor – Record EKGs at Home – Detects AFib and Irregular Arrhythmias – Instant Results in 30 Seconds – Easy to Use – Works with Most Smartphones - FSA/HSA Eligible
$79.00 (as of June 13, 2025 07:19 GMT -06:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)
Apple Watch Series 9 [GPS 41mm] Smartwatch with Storm Blue Aluminum Case with Silver Sport Band M/L. Fitness Tracker, Blood Oxygen & ECG Apps, Always-On Retina Display
(as of June 13, 2025 08:20 GMT -06:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)
Fitbit Sense 2 Advanced Health and Fitness Smartwatch with Tools to Manage Stress and Sleep, ECG App, SpO2, 24/7 Heart Rate and GPS, Shadow Grey/Graphite, One Size (S & L Bands Included)
20% Off
OMRON 2-in-1 Upper Arm Blood Pressure Monitor & 1-Lead EKG Monitor - Clinically Validated Blood Pressure Arm Cuff & Machine - Use OMRON Connect App
17% Off
Samsung Galaxy Watch 6 44mm Bluetooth Smartwatch, Fitness Tracker, Personalized HR Zones, Advanced Sleep Coaching, Heart Monitor, BIA Sensor, Health Wellness Insights, Big Screen, US Version, Graphite
53% Off $329.99 (as of June 13, 2025 07:19 GMT -06:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)
Natural Rhythm Triple Calm Magnesium 150 mg - 120 Capsules – Magnesium Complex Compound Supplement with Magnesium Glycinate, Malate, and Taurate. Calming Blend for Promoting Rest and Relaxation.
$20.77 ($0.17 / Count) (as of June 13, 2025 07:19 GMT -06:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)
Pure Encapsulations Magnesium (Glycinate) - Supplement to Support Stress Relief, Sleep, Heart Health, Nerves, Muscles, and Metabolism* - with Magnesium Glycinate - 180 Capsules
$44.60 ($0.25 / Count) (as of June 13, 2025 08:20 GMT -06:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)














![Apple Watch Series 9 [GPS 41mm] Smartwatch with Storm Blue Aluminum Case with Silver Sport Band M/L. Fitness Tracker, Blood Oxygen & ECG Apps, Always-On Retina Display #1](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/311xwtp4mFL._SL100_.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 9 [GPS 41mm] Smartwatch with Storm Blue Aluminum Case with Silver Sport Band M/L. Fitness Tracker, Blood Oxygen & ECG Apps, Always-On Retina Display #2](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/41j+8AaUGsL._SL100_.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 9 [GPS 41mm] Smartwatch with Storm Blue Aluminum Case with Silver Sport Band M/L. Fitness Tracker, Blood Oxygen & ECG Apps, Always-On Retina Display #3](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/41jIyxZitnL._SL100_.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 9 [GPS 41mm] Smartwatch with Storm Blue Aluminum Case with Silver Sport Band M/L. Fitness Tracker, Blood Oxygen & ECG Apps, Always-On Retina Display #4](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/41IpNJERjCL._SL100_.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 9 [GPS 41mm] Smartwatch with Storm Blue Aluminum Case with Silver Sport Band M/L. Fitness Tracker, Blood Oxygen & ECG Apps, Always-On Retina Display #5](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/31o17yhfYpL._SL100_.jpg)